Miscellaneous submodeling tests | ||
| ||
ProductsAbaqus/StandardAbaqus/Explicit
Using different procedures between the global model and the submodel
Elements tested
- CAX4R
- CPS3
- CPS4R
- C3D8R
- C3D8RT
Features tested
The submodeling capability is applied to different procedures between the global model and the submodel. The global procedure can be performed in Abaqus/Explicit and the submodel procedure in Abaqus/Standard or vice versa. When appropriate, a submodel boundary condition is used to adjust the time variable of the driven nodes to match the submodel analysis step time.
Problem description
The first set of problems is based on the models that are described in Two-dimensional continuum stress/displacement submodeling. In the examples used here, however, each analysis has a second compression step. The global analysis is performed in Abaqus/Explicit, and the submodel analysis is performed in Abaqus/Standard. The step times of the analyses are different. Since the Abaqus/Explicit job is quasi-static and the Abaqus/Standard job is static, the TIMESCALE parameter can be used in the submodel analysis to adjust the time variable of the driven nodes to the submodel time.
The second set of tests is based on the models that are described in Coupled temperature-displacement submodeling. The global model uses C3D8R elements, and the problem is a stress/displacement analysis. The submodel uses C3D8RT elements, and it is a coupled temperature-displacement analysis. The validity of this submodeling analysis is based on the fact that the temperature effects are relatively small at the submodel level.
The last set of problems tests the direct-integration implicit dynamic procedure with submodeling. The global analysis is performed in Abaqus/Standard, and the corresponding submodeling analysis is performed in Abaqus/Explicit, or vice-versa.
Results and discussion
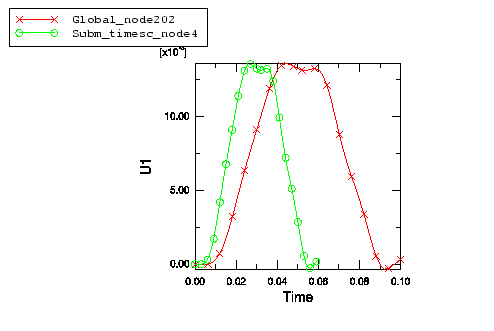
All of the driven variables are interpolated correctly from the global analysis. Figure 1 shows the effect of the TIMESCALE parameter on the amplitude formed at the driven nodes. If the analyses have the same step time, the two curves will be identical.
In the second and third set of tests the results agree well between the global model and the submodel.
Input files
- submproc_g_quasi2static_xpl.inp
-
Global, TIMESCALE parameter; Abaqus/Explicit quasi-static analysis.
- submproc_s_quasi2static_std.inp
-
Submodel, TIMESCALE parameter; Abaqus/Standard static analysis.
- submproc_s_quasi2static_std_sb.inp
-
Submodel, TYPE=SURFACE parameter; Abaqus/Standard static analysis.
- submproc_s_quasi2st_2nd_std.inp
-
Submodel, TIMESCALE parameter; second-order elements; Abaqus/Standard static analysis.
- submproc_g_dyn2tempdisp_xpl.inp
-
Global stress/displacement analysis; Abaqus/Explicit analysis.
- submproc_s_dyn2tempdisp_xpl.inp
-
Submodel coupled temperature-displacement driven by the stress/displacement model; Abaqus/Explicit analysis.
- submproc_s_dyn2tempdisp_std.inp
-
Submodel coupled temperature-displacement driven by the stress/displacement model; Abaqus/Standard analysis.
- submodelaxielem_cax4r_gd_xpl.inp
-
Global DYNAMIC analysis; Abaqus/Explicit analysis.
- submodelaxielem_cax4r_sd_std.inp
-
Submodel DYNAMIC analysis; Abaqus/Standard analysis.
- submodel2delem_cps4r_gd_std.inp
-
Global DYNAMIC analysis; Abaqus/Standard analysis.
- submodel2delem_cps4r_sd_xpl.inp
-
Submodel DYNAMIC analysis; Abaqus/Explicit analysis.
Figures
![]()
Acoustic-to-structure submodeling
Elements tested
- ACAX4R
- AC2D4R
- AC3D8R
- AC3D20
- AC3D8
- CAX4R
- CPS4R
- C3D8R
- C3D8
- C3D20
- SAX1
- S4R
- S8R
Features tested
The submodeling capability is applied to the coupled acoustic-structural models. The global procedure is performed as a fully coupled acoustic-structural analysis in which the two media are coupled through the use of a tie constraint. Submodeling is performed on the structural component of the global model by using the acoustic pressure from a global acoustic structural model.
Problem description
In the global analysis acoustic pressure acts on either one or both sides of a flat panel. The flat panel is modeled using shell or solid elements. When the pressure acts on both sides of the panel, the correct side from which the acoustic pressures are to be interpolated is specified (see Node-based submodeling). The fluid and the structure in the global model have the material properties of water and steel, respectively. The submodel has the material properties of steel. For Abaqus/Standard the direct-integration implicit dynamic and the steady-state dynamic (direct and mode-based) procedures have been used in separate tests.
Results and discussion
The loads resulting from the interpolated acoustic pressure from the global analysis are applied correctly on the structure for the single-sided as well as for the double-sided pressure cases.
Input files
Abaqus/Standard Input files
- ac2solid_g_c3d20_ac3d20_std.inp
-
Global analysis using DYNAMIC; fluid on one side; AC3D20 and C3D20 elements.
- ac2solid_s_c3d20_ac3d20_std.inp
-
Submodel analysis using DYNAMIC; submodel driven on one side by acoustic pressure and on the second side by displacements; C3D20 elements.
- ac2solid_g_c3d8_ac3d8_std.inp
-
Global analysis using DYNAMIC; fluid on one side; AC3D8 and C3D8 elements.
- ac2solid_s_c3d8_ac3d8_std.inp
-
Submodel analysis using DYNAMIC; submodel driven on one side by acoustic pressure and on the second side by displacements; C3D8 elements.
- ac2solid_g_s4_ac3d8_std.inp
-
Global analysis using DYNAMIC; fluid on two sides; S4 and AC3D8 elements.
- ac2solid_s_s4_ac3d8_std.inp
-
Submodel analysis using DYNAMIC; submodel driven on both sides by the acoustic pressure; S4 elements.
- ac2solid_s_s8r_ac3d8_std.inp
-
Submodel analysis using DYNAMIC; submodel driven on both sides by the acoustic pressure; S8R elements.
- ac2solid_g_c3d8_ac3d8_ssd.inp
-
Global analysis using STEADY STATE DYNAMICS, DIRECT; fluid on one side; AC3D8 and C3D8 elements.
- ac2solid_s_c3d8_ac3d8_ssd.inp
-
Submodel analysis using STEADY STATE DYNAMICS, DIRECT; submodel driven on one side by acoustic pressure and on the second side by displacements; C3D8 elements.
Abaqus/Explicit Input files
- ac2solid_g_c3d8r_ac3d8r_xpl.inp
-
Global analysis; fluid on one side; AC3D8R and C3D8R elements.
- ac2solid_s_c3d8r_ac3d8r_xpl.inp
-
Submodel analysis; submodel driven on one side by acoustic pressure and on the second side by displacements; C3D8R elements.
- ac2solid_g_s4r_ac3d8r_xpl.inp
-
Global analysis; fluid on two sides; S4R and AC3D8R elements.
- ac2solid_s_s4r_ac3d8r_xpl.inp
-
Submodel analysis; submodel driven on both sides by the acoustic pressure; S4R elements.
- ac2solid_g_cax4r_acax4r_xpl.inp
-
Global analysis; fluid on one side; CAX4R and ACAX4R elements.
- ac2solid_s_cax4r_acax4r_xpl.inp
-
Submodel analysis; submodel driven on one side by acoustic pressure and on the second side by displacements; CAX4R elements.
- ac2solid_g_sax1_acax4r_xpl.inp
-
Global analysis; fluid on two sides; SAX1 and ACAX4R elements.
- ac2solid_s_sax1_acax4r_xpl.inp
-
Submodel analysis; submodel driven on both sides by the acoustic pressure; SAX1 elements.
- ac2solid_g_cps4r_ac2d4r_xpl.inp
-
Global analysis; fluid on one side; CPS4R and AC2D4R elements.
- ac2solid_s_cps4r_ac2d4r_xpl.inp
-
Submodel analysis; submodel driven on one side by acoustic pressure and on the second side by displacements; CPS4R elements.
![]()
intersection Only submodeling
Elements tested
- C3D8
- C3D8P
- C3D8R
Features tested
The submodeling capability is applied using the intersection-only feature, where nodes not found in the global model are ignored rather than labeled as errors.
Problem description
A simple model of a rectangular prism is used. The global model and submodel geometries are identical, but the submodel is shifted in space so that the intersection of the models represents a subset of the submodel geometry. All nodes in the submodel are identified as driven nodes.
Results and discussion
The results show that submodel boundary conditions are applied to driven nodes lying within the global model, while driven nodes lying outside the global model have no submodel boundary condition applied.
Input files
Abaqus/Standard Input files
- subm_intonly_g_c3d8_std.inp
-
Global analysis using C3D8 elements.
- subm_intonly_s_c3d8_std.inp
-
Submodel analysis using C3D8 elements and driven displacements.
- subm_intonly_rs_c3d8_std.inp
-
Submodel restart analysis using C3D8 elements and driven displacements.
- subm_intonly_g_c3d8p_std.inp
-
Global analysis using C3D8P elements.
- subm_intonly_s_c3d8p_std.inp
-
Submodel analysis using C3D8P elements and driven displacements and pore pressures.
Abaqus/Explicit Input files
- subm_intonly_g_c3d8r_xpl.inp
-
Global analysis using C3D8R elements.
- subm_intonly_s_c3d8r_xpl.inp
-
Submodel analysis using C3D8R elements and driven displacements.