What do single-headed and double-headed arrows represent? | |||||
|
| ||||
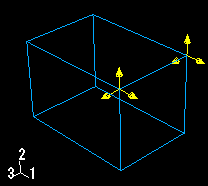
An arrow with a single arrowhead represents a component of a prescribed condition that is applied to a translational degree of freedom. For example, the three components of the concentrated force in Figure 1 are applied to degrees of freedom 1 through 3; therefore, each arrow in the figure has a single arrowhead.
When a component of a prescribed condition is applied to a rotational degree of freedom, that component appears as a double-headed arrow. The arrows in Figure 2 indicate that a Velocity/Angular Velocity boundary condition is applied to degrees of freedom 4 and 6 of the vertices.
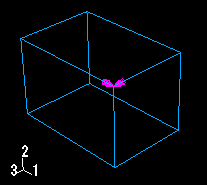
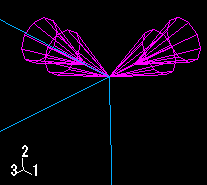
A magnified view of the double-headed arrows appears in Figure 3.
If you apply a prescribed condition to both translational and rotational degrees of freedom, both the single-headed and the double-headed arrows appear. For example, a Velocity/Angular Velocity boundary condition is applied to degrees of freedom 1, 3, 4, and 6 of the vertex in Figure 4.
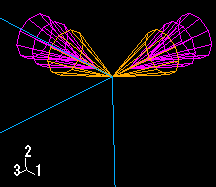
In this figure the single-headed arrows are sandy brown and indicate that degrees of freedom 1 and 3 of the vertex are fixed.The double-headed arrows are magenta and appear directly behind the single-headed arrows; the double-headed arrows indicate that degrees of freedom 4 and 6 of the vertex are fixed.
For information on arrow color, see Understanding prescribed condition symbol type, color, and size. For information on when to expect arrows to point toward or away from a region, see Understanding symbol location and direction.