Creating a model with cohesive elements using geometry and mesh tools | ||
| ||
In the Part module, define the geometry of the model. You should define the geometric region that represents the cohesive layer as a solid, even if the thickness of the layer is close to zero. To avoid numerical problems, it is recommended that you model the geometry using a value of 10−4 or greater for the thickness. If the actual thickness of the layer is less than this value, you should specify the actual thickness in the Initial thickness field of the cohesive section editor as described in Creating cohesive sections
In the Mesh module, mesh the surrounding bulk material. You can use any of the mesh tools to mesh the surrounding bulk material. See Mesh generation, for more information.
In the Mesh module, mesh the cohesive region using one of the following methods:
- Two- and three-dimensional models
Top-down swept or bottom-up meshing technique. You can assign the top-down swept meshing technique or the bottom-up meshing technique to mesh the cohesive region. The bottom-up meshing technique is available only for three-dimensional models (for more information, see Bottom-up meshing). Regardless of the meshing technique that you choose, you must sweep, extrude, or revolve the mesh in the thickness direction of the element to produce the correct element orientation. For a complex cohesive region, you may need to partition the model to create a group of sweep regions that you can align consistently. For more information, see Selecting a meshing technique, and Specifying the sweep path.
- Three-dimensional models
Convert the cohesive region into a shell region, and use the offset meshing technique.
Convert the solid part to a shell using the From solid shell tool in the Part module.
Isolate a collection of faces that represents an idealized shell of the part using the Remove faces tool in the Geometry Edit toolset.
Mesh the simplified model with shell elements, and create a mesh part.
Use the mesh part to generate an offset mesh of solid hexahedral or wedge elements. The elements will be oriented through the thickness of the part, and you can verify this with the Query toolset.
For detailed instructions, see Generating layers of solid elements offset from an existing mesh.
In the Mesh module, use the element type assignment tool to assign the cohesive element type to the cohesive region. See Element type assignment, for more information.
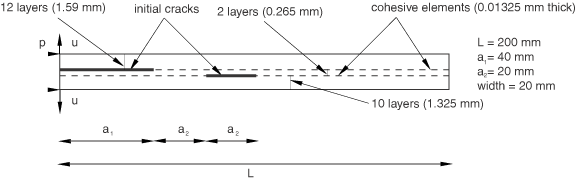
For example, Figure 1 illustrates the layered composite specimen that is used in the benchmark problem Delamination analysis of laminated composites. An Abaqus Scripting Interface script that reproduces the composite specimen model using Abaqus/CAE is provided with this problem.