Connecting lug with plasticity analysis | ||
| ||
The results from the linear analysis indicate that the lug will yield. You need to determine the extent of the plastic deformation in the lug and the magnitude of the plastic strains so that you can assess whether or not the lug will fail. You do not need to consider inertial effects in this analysis; thus, you will use Abaqus/Standard to examine the static response of the lug.
The only inelastic material data available for the steel are its yield stress (380 MPa) and its strain at failure (0.15). You decide to assume that the steel is perfectly plastic: the material does not harden, and the stress can never exceed 380 MPa (see Figure 1).
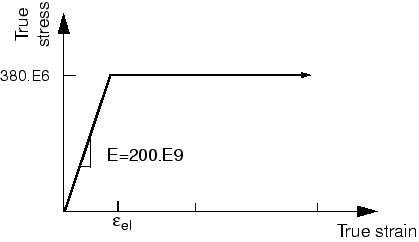
In reality some hardening will probably occur, but this assumption is conservative; if the material hardens, the plastic strains will be less than those predicted by the simulation.
Abaqus provides scripts that replicate the complete analysis model for this problem. Run one of these scripts if you encounter difficulties following the instructions given below or if you wish to check your work. Scripts are available in the following locations:
-
A Python script for this example is provided in Connecting lug with plasticity. Instructions on how to fetch the script and run it within Abaqus/CAE are given in Example Files.
-
A plug-in script for this example is available in the Abaqus/CAE Plug-in toolset. To run the script from Abaqus/CAE, select ; highlight Connecting lug with plasticity; and click . For more information about the Getting Started plug-ins, see Running the Getting Started with Abaqus examples.