Interpolating an X–Y data object | ||||
|
| |||
Context:
Figure 1 shows an example of an X–Y plot produced using the function, superimposed over the raw data.
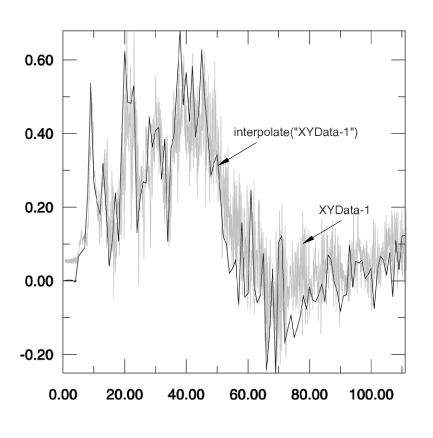
The name of the X–Y data object is the only required argument for the function. A description of the optional arguments follows:
The X-axis increment between interpolated data points (xIncrement). If you do not specify a value for this argument or if you specify a non-positive value, Abaqus/CAE uses the minimum X-increment of the raw data set.
A symbolic constant that specifies the interpolation scheme (interpolation). Valid values for this argument are QUADRATIC, specifying a Lagrange second-order interpolation scheme; CUBIC_SPLINE, specifying a cubic spline interpolation scheme; and LINEAR, specifying a linear interpolation scheme. The default value is QUADRATIC.
The slope of the raw data curve leading up to the first data point (startslope). This argument's default value is 0.0 (for a level slope), and it is used only when interpolation=CUBIC_SPLINE.
The slope of the raw data curve continuing past the final data point (endslope). This argument's default value is 0.0 (for a level slope), and it is used only when interpolation=CUBIC_SPLINE.