Context:
(Some procedures—for example, heat transfer—do not write nodal vector quantities to the output database by default and do not select a variable as the default deformed variable. Therefore, Abaqus cannot display a deformed plot, since in such cases the output database does not contain any variables that can be used to compute a deformed shape.)
From the main menu bar, select .
Abaqus displays the deformed model in the same increment and step that it last displayed the undeformed model. The element labels also appear because the common plot options were used to display them.
Open the Common Plot Options dialog box. Click Defaults followed by Apply to restore and apply the default options.
The state block indicates the default deformed variable being plotted (U) and the deformation scale factor (1.000e+00). Abaqus selects a default deformation scale factor of 1.0 for large-displacement analyses. (For small-displacement analyses Abaqus chooses the default scale factor to fit the viewport optimally.)
The buttons in the context bar allow you to move between frames of the analysis. In particular, the button on the far right of the context bar is the frame selector  tool; it allows you to drag a slider to choose the frame of interest.
tool; it allows you to drag a slider to choose the frame of interest.
You can also move directly to a selected step and increment using the following technique:
- From the main menu bar, select .
Abaqus displays the Step/Frame dialog box.
- Select Step 1, Increment 0, and click Apply.
- The Step/Frame dialog box also displays the step time associated with an increment. Use the Step/Frame dialog box to display the deformed model approximately halfway through the second step.
Use a combination of the buttons in the context bar and the Step/Frame dialog box to view the deformed plot in different frames and in different steps.
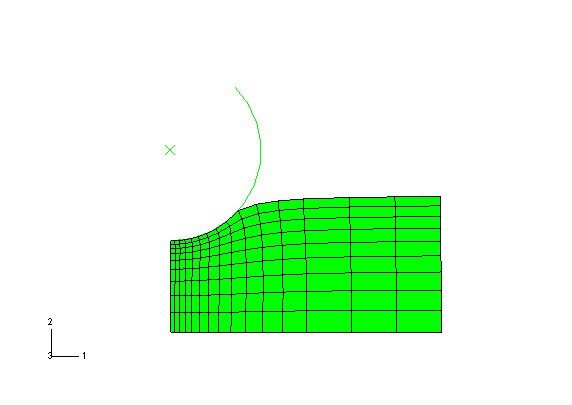
Display the deformed model after the last increment of the third step (Step 3 and Step Time = 10.00), as shown in Figure 1.
Click Cancel to close the Step/Frame dialog box.
 tool in
tool in  tool; it allows you to drag a slider to choose the frame of interest.
tool; it allows you to drag a slider to choose the frame of interest.