Postprocessing | ||
| ||
- Deformed model shape and contour plots
-
The basic results of this simulation are the deformation of the joint and the stresses caused by the shearing process. Plot the deformed model shape and the Mises stress, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively.
Figure 1. Deformed model shape.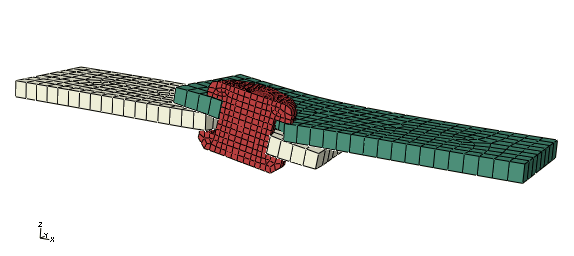
Figure 2. Mises stress.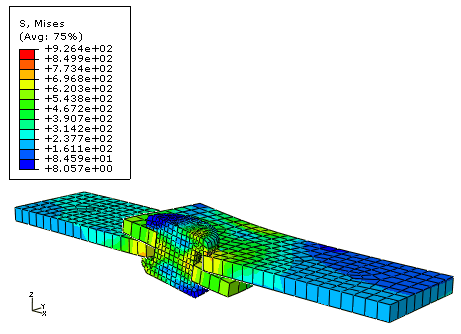
- Contact pressures
-
You will now plot the contact pressures in the lap joint.
Since it is difficult to see contact pressures when the entire model is displayed, use the Display Groups toolbar to display only the top plate in the viewport.
Create a path plot to examine the variation of the contact pressure around the bolt hole of the top plate.
To create a path plot:
-
In the Results Tree, double-click Paths. In the Create Path dialog box, select Edge list as the type and click Continue.
-
In the Edit Edge List Path dialog box, select the instance corresponding to the top plate and click Add After.
-
In the prompt area, select by shortest distance as the selection method.
-
In the viewport, select the edge at the left end of the bolt hole as the starting edge of the path and the node at the right end of the bolt hole as the end node of the path, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Path definition.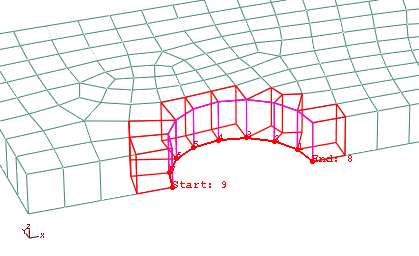
-
Click in the prompt area to indicate that you have finished making selections for the path. Click to save the path definition and to close the Edit Edge List Path dialog box.
-
In the Results Tree, double-click XYData. Select Path in the Create XY Data dialog box, and click Continue.
-
In the Y Values frame of the XY Data from Path dialog box, click Step/Frame. In the Step/Frame dialog box, select the last frame of the step. Click OK to close the Step/Frame dialog box.
-
Make sure that the field output variable is set to CPRESS, and click Plot to view the path plot. Click Save As to save the plot.
The path plot appears as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. CPRESS distribution around the bolt hole in top plate.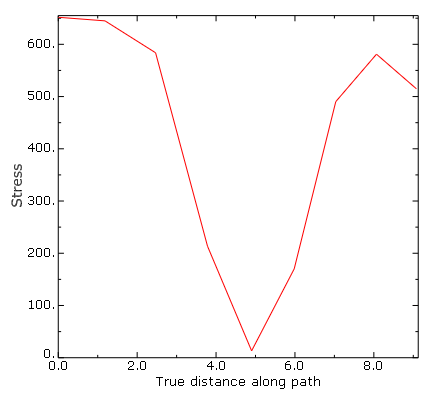
-