Application of boundary conditions and load | ||
| ||
You will apply the following boundary conditions and load:
-
A boundary condition called Fixed that constrains all degrees of freedom at the end of the hinge piece with the lubrication hole, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. One end of the hinge is constrained.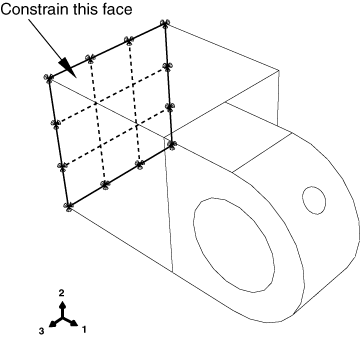
-
A boundary condition called NoSlip that constrains all degrees of freedom of the pin while contact is established during the first analysis step. You will modify this boundary condition in the second analysis step (the step in which the load is applied) so that degrees of freedom 1 and 5 are unconstrained. Figure 2 illustrates this boundary condition applied at the reference point.
Figure 2. The pin is constrained.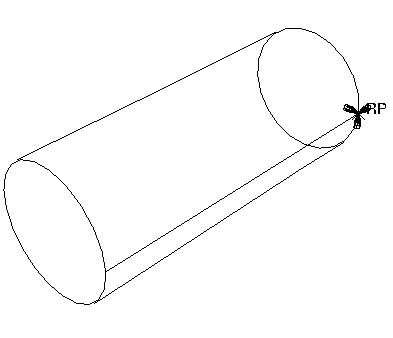
-
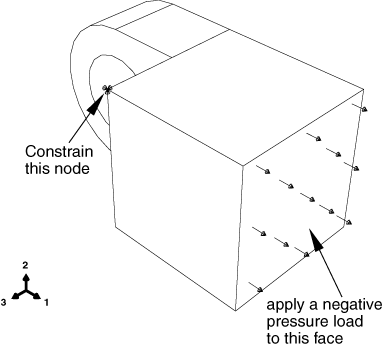
A boundary condition called Constrain that constrains all degrees of freedom of a point on the solid hinge piece during the first analysis step. You will modify this boundary condition in the second analysis step so that degree of freedom 1 is unconstrained when the load is applied.
-
A load called Pressure that you apply to the end of the solid hinge piece during the second analysis step. Figure 3 illustrates the constraint and the pressure load applied to the solid hinge.
Figure 3. The second hinge is constrained and loaded.