Applying loads and boundary conditions | ||
| ||
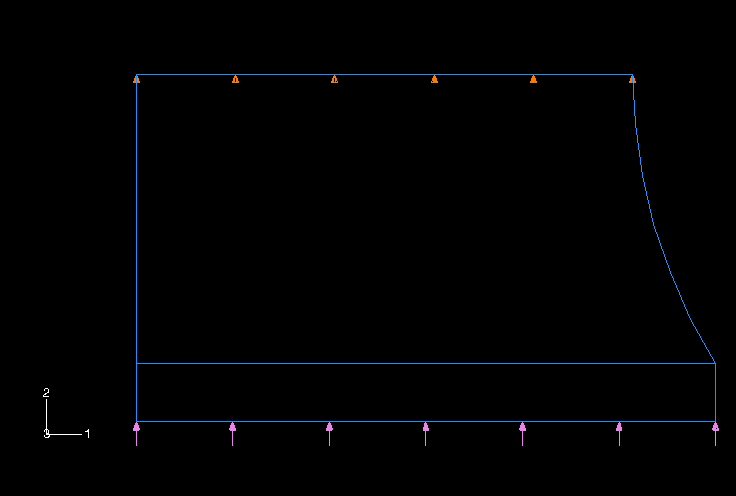
No boundary constraints are needed in the radial direction (global 1-direction) because the axisymmetric nature of the model does not allow the structure to move as a rigid body in the radial direction. Abaqus will allow nodes to move in the radial direction, even those initially on the axis of symmetry (i.e., those with a radial coordinate of 0.0), if no boundary conditions are applied to their radial displacements (degree of freedom 1). Since you want to let the mount deform radially in this analysis, do not apply any boundary conditions; again, Abaqus will prevent rigid body motions automatically.
The mount must carry a maximum axial load of 5.5 kN, spread uniformly over the steel plates. Therefore, apply a distributed load to the bottom of the steel plate, as shown in Figure 1. The magnitude of the pressure is given by