ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
ProductsAbaqus/ExplicitAbaqus/CAE
Description
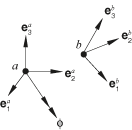
The ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER connection does not impose kinematic constraints. It defines three local directions at node a and three local directions at node b. The ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER connection's formulation is similar to that for the ROTATION connection. The ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER connection measures the finite rotation that takes the local directions at node a into the local directions at node b and parameterizes that finite rotation by the rotation vector. Let be the rotation vector that positions local directions relative to ; that is,
for all , where is the skew-symmetric matrix with axial vector . See Rotation variables for a discussion of finite rotations. The connection measures the change in the rotation vector components in the local directions rotating with the body at node b. The rotation vector components are calculated as
There are no available components of relative motion for the ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER connection. The connector rotation is
where is the initial rotation vector and is an integer accounting for rotations with magnitude greater than .
The ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER connection differs from the ROTATION connection in the way angular velocity and acceleration are calculated. The ROTATION-ACCELEROMETER connection measures velocity and acceleration from the nodes as
where , , , and are the nodal angular velocities and accelerations at nodes a and b, respectively.
In two-dimensional and axisymmetric analyses .
![]()
Summary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||