How does the Abaqus Scripting Interface interact with Abaqus/CAE? | ||
| ||
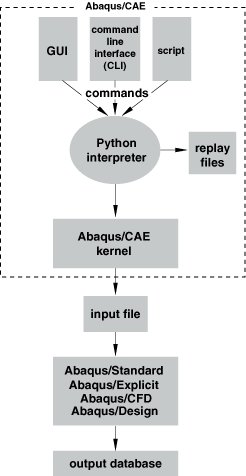
Abaqus Scripting Interface commands can be issued to the Abaqus/CAE kernel from one of the following:
The graphical user interface (GUI). For example, when you click or in a dialog box, the GUI generates a command based on your options and settings in the dialog box. You can use the Macro Manager to record a sequence of the generated Abaqus Scripting Interface commands in a macro file. For more information, see Creating and running a macro.
Click
 in the lower left corner of the main window to display the command line interface (CLI). You can type a single command or paste in a sequence of commands from another window; the command is executed when you press Enter. You can type any Python command into the command line; for example, you can use the command line as a simple calculator.
in the lower left corner of the main window to display the command line interface (CLI). You can type a single command or paste in a sequence of commands from another window; the command is executed when you press Enter. You can type any Python command into the command line; for example, you can use the command line as a simple calculator. Note:
When you are using Abaqus/CAE, errors and messages are posted into the message area. Click
 in the lower left corner of the main window to display the message area.
in the lower left corner of the main window to display the message area.If you have more than a few commands to execute or if you are repeatedly executing the same commands, it may be more convenient to store the set of statements in a file called a script. A script contains a sequence of Python statements stored in plain ASCII format. For example, you might create a script that opens an output database, displays a contour plot of a selected variable, customizes the legend of the contour plot, and prints the resulting image on a local PostScript printer. In addition, scripts are useful for starting Abaqus/CAE in a predetermined state. For example, you can define a standard configuration for printing, create remote queues, and define a set of standard materials and their properties.
You can use one of the following methods to run a script:
- Running a script when you start Abaqus/CAE
You can run a script when you start an Abaqus/CAE session by typing the following command:
abaqus cae script=myscript.py
where myscript.py is the name of the file containing the script. The equivalent command for Abaqus/Viewer is
abaqus viewer script=myscript.py
Arguments can be passed into the script by entering -- on the command line, followed by the arguments separated by one or more spaces. These arguments will be ignored by the Abaqus/CAE execution procedure, but they will be accessible within the script. For more information, see Abaqus/CAE execution, and Abaqus/Viewer execution.
- Running a script without the Abaqus/CAE GUI
You can run a script without the Abaqus/CAE GUI by typing the following command:
abaqus cae noGUI=myscript.py
where myscript.py is the name of the file containing the script. The equivalent command for Abaqus/Viewer is
abaqus viewer noGUI=myscript.py
The Abaqus/CAE kernel is started without the GUI. Running a script without the Abaqus/CAE GUI is useful for automating pre- or postanalysis processing tasks without the added expense of running a display. When the script finishes running, the Abaqus/CAE kernel terminates. If you execute a script without the GUI, the script cannot interact with the user, monitor jobs, or generate animations. When running a script without the user interface, jobs are always run interactively. If a job queue is specified, it will be ignored.
- Running a script from the startup screen
When you start an Abaqus/CAE session, Abaqus displays the startup screen. You can run a script from the startup screen by clicking . Abaqus displays the Run Script dialog box, and you select the file containing the script.
- Running a script from the menu
You can run a script by selecting from the main menu bar. Abaqus displays the Run Script dialog box, and you select the file containing the script.
- Running a script from the command line interface
You can run a script from the command line interface (CLI) by typing the following command:
execfile('myscript.py')where myscript.py is the name of the file containing the script and the file in this example is in the current directory. Figure 2 shows an example script being run from the command line interface.
Figure 2. Scripts can be run from the command line interface.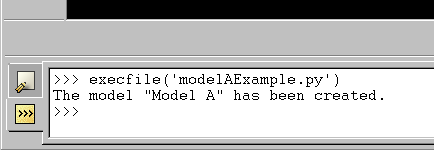
Click
 in the lower left corner of the main window to switch from the message area to the command line interface.
in the lower left corner of the main window to switch from the message area to the command line interface.