Defining a loft path | ||
| ||
When you create a loft feature, you can choose from the following methods to define a loft path:
- Specify tangencies
Specify tangencies is the default loft path definition. If you select Specify tangencies, Abaqus/CAE creates a single smooth path that passes through the center of each loft section, as shown in Figure 1. You can apply tangency conditions that modify the shape of the loft near the starting and ending loft sections. For more information on loft tangency, see Defining loft tangency.
Figure 1. A loft feature with a path defined by Abaqus/CAE.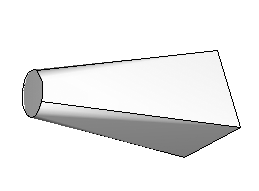
- Select path
If you choose Select path, you can select from existing edges to define a loft path. This method also allows you to define multiple loft paths. The loft feature is created by following the loft paths as they connect one loft section to the next, as shown in Figure 2. A loft feature with a single selected path behaves similarly to a swept feature except that the cross-section of the loft is constantly changing to match the position and shape of the next loft section along the path.
Figure 2. A loft feature with a single user-defined path.
You must pick from existing line segments in the viewport to create paths connecting all of the loft sections. Each path must be a smooth curve, and it must connect the sections in the same order that they will be connected when the loft is created. You can use the
 tool to create spline wires that define the three-dimensional paths. For more information, see Adding a point-to-point wire feature.
tool to create spline wires that define the three-dimensional paths. For more information, see Adding a point-to-point wire feature.
Once the loft feature is created, you cannot edit the paths directly, regardless of which path definition you chose. However, if you used Select path, you can edit the points that created each spline wire by using the Feature Manipulation toolset to edit the features that created the wire vertices.