Understanding how to overlay plots | ||
| ||
combine a contour plot and an X–Y plot
compare the deformed plot shapes from two different output database files in the same viewport
combine a time history animation with an animated X–Y plot displaying the change in several variables in the model over time
Overlay plots are useful, for example, for displaying data from both output databases in a co-simulation in the same viewport.
Overlay plots are composed of layers; each layer contains one plot, and the layers are stacked on top of each other to create the combined plot. Figure 1 shows a plot containing the deformed shape plots at four different increments of an analysis as well as an X–Y plot of the strain energy in the model versus time.
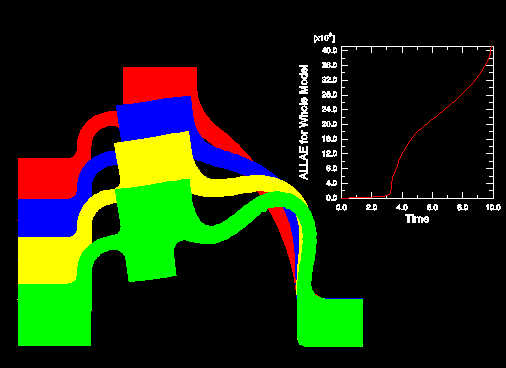
By default, the viewport does not contain any layers; only one plot at a time is displayed. To overlay multiple plots, you create a layer for each individual plot as you interact with Abaqus/CAE. You then choose the layers to display in the current viewport. You can create as many layers as you would like; any number of layers can be displayed in the same viewport. In addition, you can open multiple output databases and automatically display the combined contents in an overlay plot in a single viewport.
Use the Overlay Plot Layer Manager to create, display, position, and delete layers. To access the manager, select from the main menu bar or click the Overlay Plot Layer Manager  tool in the toolbox.
tool in the toolbox.
When you create a layer, it contains everything that is visible in the current viewport. You can change the contents of a layer, manipulate its view, reorder the layer with respect to the other layers in the overlay plot, and change the various display options that are applied to the contents. By default, layers are plotted directly on top of one another. Sometimes lines that appear directly on top of one another can create undesirable visual effects. You can offset the layers with respect to each other to avoid such display anomalies.
The settings in the Overlay Plot Layer Manager are applied to the contents of the current viewport only when you click . Abaqus/CAE then enters the overlay plot state; when you click in the Overlay Plot Layer Manager, the overlay plot disappears from the viewport and the display reverts back to the previous plot state. You can also click the  tool in the toolbox to switch between the single plot and overlay plot state at any time.
tool in the toolbox to switch between the single plot and overlay plot state at any time.
When you are in the overlay plot state, Abaqus/CAE displays your plots relative to an overlay plot coordinate system. As you create a layer, Abaqus/CAE assigns the view in which the layer was created to the overlay plot front (1–2) view. You can modify what is displayed in the overlay plot front view by manipulating the view for each individual layer, as described in Manipulating the view for an overlay plot. User-specified views defined in the overlay plot state are relative to the overlay plot coordinate system.
Columns in the Overlay Plot Layer Manager display the following information about each layer:
- Visible
A check mark in this column indicates that the layer is visible in the viewport when you are in the overlay plot state.
- Current
A check mark in this column indicates that the layer is current. Only one layer can be current at a time, although each layer can contain multiple plot states (for more information, see Displaying multiple plot states). Plot options are applied to only the current layer when you are in the overlay plot state; you can choose whether view manipulation options are applied to all existing layers or to only the current layer. The current layer is not necessarily the foremost layer in the viewport.
- Name
The name of the layer.
- Object
The name of the object contained in the layer; for example, an output database or an X–Y plot.