When will Abaqus/CAE delete a mesh? | ||||||
|
| |||||
Seeding
Element shape
Meshing technique
Meshing algorithm
Logical corners of a two-dimensional structured region
Transition control
Sweep path of a swept region
If you change any of the attributes listed, the existing mesh will no longer be consistent with its attributes. As a result, Abaqus/CAE deletes the mesh, and you can recreate a new mesh that matches the new attributes. (Element order and element family are the only attributes that, when changed, do not require the mesh to be deleted and recreated.)
Whenever you make a change that will affect any of these attributes for a top-down meshed region, Abaqus/CAE displays a dialog box similar to the one shown in Figure 1.
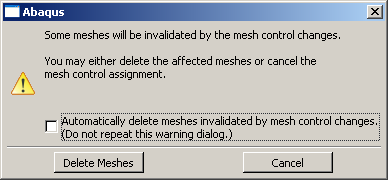
You can delete the mesh by clicking the button, or you can keep your mesh and exit the procedure by pressing the button.
You can also avoid this warning message for the remainder of the current session by toggling Automatically delete meshes invalidated by mesh control changes. The next time you attempt to change the attributes of a part, part instance, or region that already contains a mesh, the mesh will be deleted immediately without any warning being displayed.
If you save your model to a model database before you delete the mesh, you can revert back to that mesh if you are dissatisfied with later meshing attempts.
Since bottom-up meshes can be very time consuming to create, Abaqus/CAE attempts to preserve them in many circumstances that would cause a top-down mesh to be deleted. Bottom-up meshes are retained during changes to seeding, partitioning, and virtual topology. When you partition a region or create a virtual topology feature the mesh will be retained, but associativity with the geometry effected by the partition or virtual topology operation will be lost.
| Warning:
There is no way to avoid deleting a top-down mesh when you change one of the meshing attributes listed above. Likewise, if you change the part geometry, Abaqus/CAE always deletes both top-down and bottom-up meshes without warning. Since remeshing can be time consuming for large or complex models, you should use caution when changing these attributes. |
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on deleting a mesh, see Deleting a mesh.