SLIDE-PLANE | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
ProductsAbaqus/StandardAbaqus/ExplicitAbaqus/CAE
Description
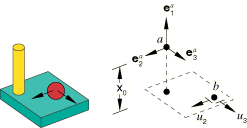
The SLIDE-PLANE connection constrains the position of node b, , to remain on a plane defined by the local normal direction . The normal direction distance from node a to the plane is constant:
where is the initial distance from node a to the plane. The constraint force in the SLIDE-PLANE connection is
Node b can move in the plane defined by the normal of node a. The position of node b in the plane relative to node a is
The two available components of relative motion, and , are
where and are the coordinates of the initial position of node b. The connector constitutive displacements are
The kinetic force in the plane is
![]()
Friction
Predefined Coulomb-like friction in the SLIDE-PLANE connection relates the kinematic constraint forces in the connector to the friction forces (CSFC) in the translations along the two local directions in the 2–3 plane.
The frictional effect is formally written as
where the potential represents the magnitude of the frictional tangential tractions in the connector in a direction tangent to the 2–3 plane on which contact occurs, is the friction-producing normal force on the same plane, and is the friction coefficient. Frictional stick occurs if ; and sliding occurs if , in which case the friction force is .
The normal force is the sum of a magnitude measure of friction-producing connector forces, , and a self-equilibrated internal contact force, :
The force magnitude .
The magnitude of the frictional tangential tractions, is computed using
The predefined Coulomb-like friction is computed differently when the SLIDE-PLANE connection is used in combination with a REVOLUTE connection. See the description of the PLANAR connection for the predefined friction definition in this case.
![]()
Summary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||