RADIAL-THRUST | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
ProductsAbaqus/StandardAbaqus/ExplicitAbaqus/CAE
Description
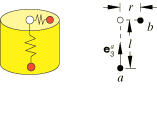
The RADIAL-THRUST connection does not impose kinematic constraints. An orientation at node a is required to define the axis of the rectangular coordinate system, . The position of node b relative to node a is given by the radial and axial-direction distances
The RADIAL-THRUST connection has two available components of relative motion, and . The radial displacement measures the change in distance from node b to the axis of the cylindrical coordinate system and is defined as
where is the initial radial distance from node b to the axis. The thrust displacement measures the change in distance from node a to node b along the cylindrical axis and is defined as
where is the initial distance along the axis from node b to node a. The connector constitutive displacements are
The kinetic force is
where the radial unit vector is
The radial resistance of the RADIAL-THRUST connector is analogous to a single spring in the – plane. Loads applied in this plane and perpendicular to the current radial unit vector will initially encounter no resistance and may lead to numerical singularity and/or zero pivot warnings from the solver during static analyses. If the numerical singularities cause convergence difficulties, one modeling option is to overlay the RADIAL-THRUST connector with a CARTESIAN connector with a very small elastic stiffness.
![]()
Summary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||