CONSTANT VELOCITY | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
ProductsAbaqus/StandardAbaqus/ExplicitAbaqus/CAE
Description
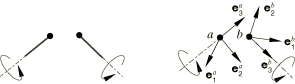
The shaft direction at node a is , and the shaft direction at node b is . The constant velocity constraint is stated as follows. In any configuration there are two unit length orthogonal vectors and in the plane perpendicular to the shaft at node b. These vectors can be written
The angle is chosen such that
The constant velocity constraint requires that the angle is constant at all times. The constant velocity constraint is equivalent to constraining the torsion angle to be constant in a FLEXION-TORSION connection.
The name “constant velocity” for this connection type derives from the following property. If the angular velocities of the two shafts, and , have components only along each shaft, respectively, and in the direction of the normal to the plane containing the two shafts (that is, along the direction), the components of angular velocity along the respective shaft directions are equal:
Hence, the “spinning” angular velocity component is the same about each shaft.
The constraint moment imposing the constant velocity constraint has a single component about the average shaft direction and is written
![]()
Summary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||